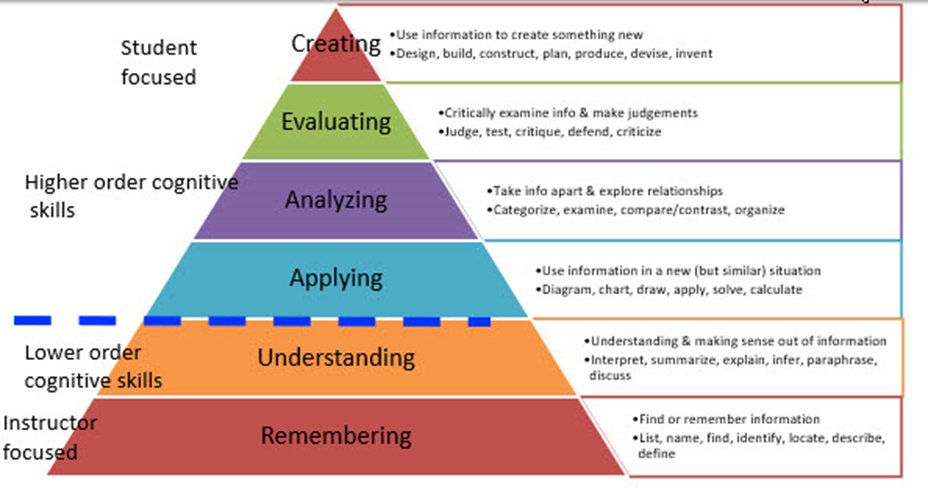
In the 1950’s, Benjamin Bloom and colleagues developed a method for the classification of educational goals and learning objectives, commonly referred to as “Bloom’s taxonomy.” While it should be noted that other educational taxonomies and hierarchical systems for the cognitive domain have been developed, Bloom’s taxonomy remains the best known. The taxonomy is a 6-tiered hierarchical model to classify thinking according to levels of complexity.
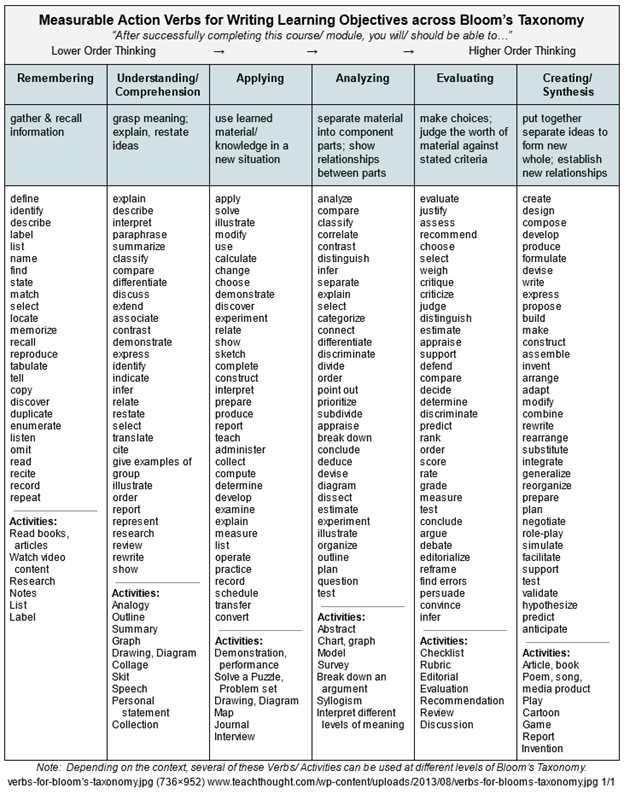
Given that learning objectives should be measurable, often defined by the verb contained in the objective, different measurable verbs are often associated with each Bloom’s level. Each level is also associated with different types of assessments but the design of an assessment can alter the level measured.