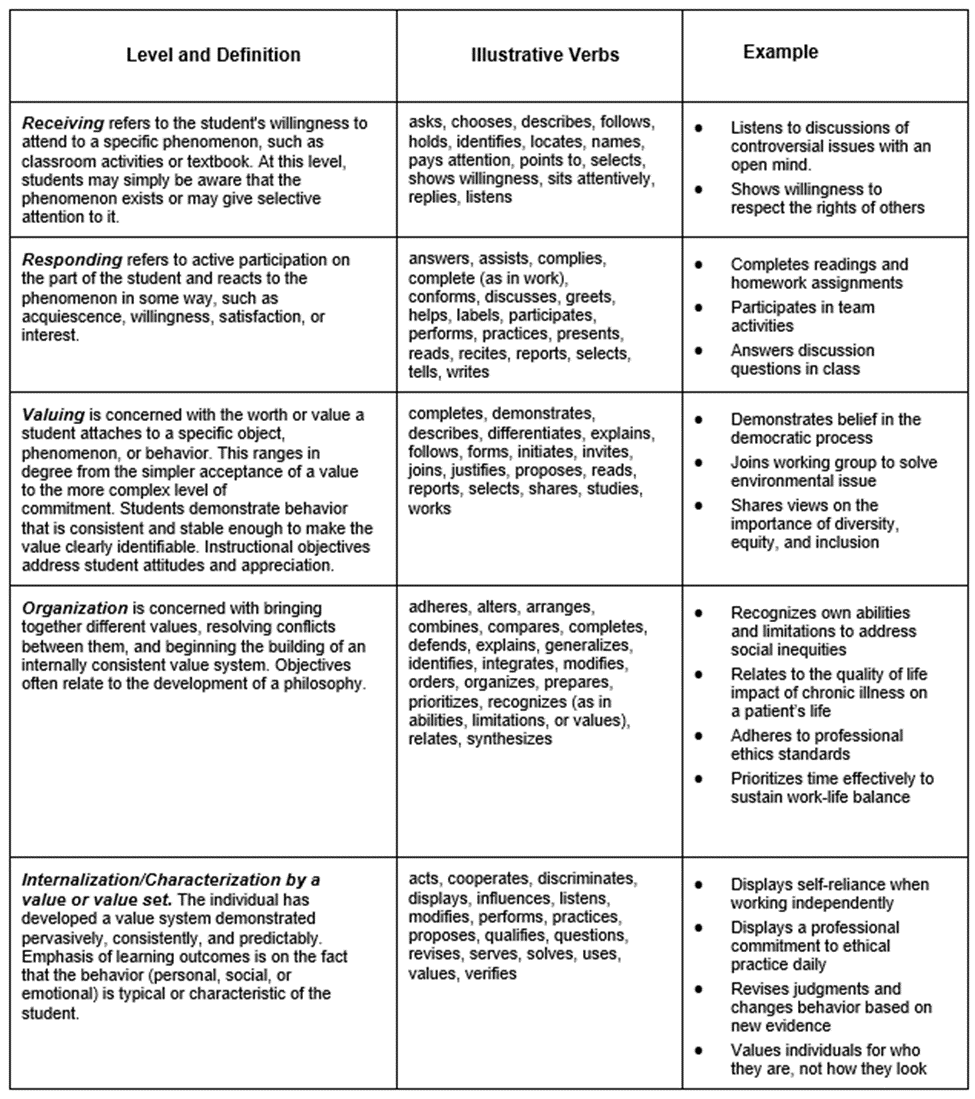
Affective learning is demonstrated by behaviors indicating attitudes of awareness, interest, attention, concern, and responsibility, ability to listen and respond in interactions with others, and ability to demonstrate those attitudinal characteristics or values which are appropriate to the situation and the field of study.
Krathwohl’s affective domain taxonomy, a commonly used taxonomy for defining affective learning objectives, is a hierarchical structure. At the lowest level learners are generally aware of a particular phenomenon but can advance to the highest level at which learners now characterize the value because they have internalized it into their own value system.
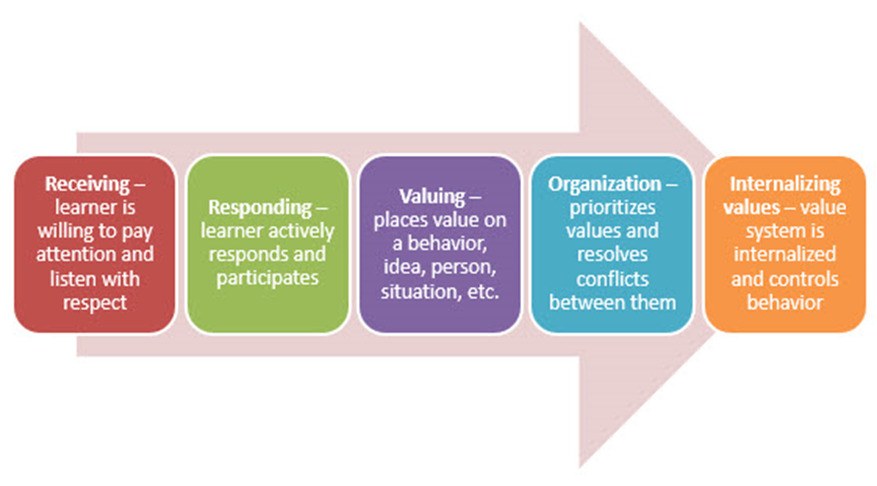
As with the cognitive and psychomotor taxonomies, each level of Krathwohl’s taxonomy is associated with verbs typically utilized to describe its level of valuing.